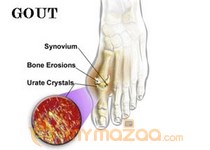
Gout is a painful disease of the joints, which usually affects the big toe first in most people. It is caused by too much uric acid in the blood. Uric acid is formed by the breakdown of chemicals called purines, which can lead to high levels of uric acid and cause many problems such as joint swelling and kidney stones. Normally the uric acid is dissolved in the blood and passes out via the kidneys into the urine but if this does not occur it can build up in the body and cause the crystals to deposit and cause gout.
Some genetic diseases affect the breakdown of uric acid and also cause it to build up. Other causes include exposure to lead, foods high animal protein, some medications, obesity, excess alcohol or foods rich in purines. Some foods that cause gout are organ meats such as liver, brain and kidneys. Other foods include herring, anchovies, peas and dried beans. Alcohol affects the elimination of uric acid especially when taken in excess.
Medications such as diuretics (which help the kidney eliminate more urine) or aspirin cause gout. And people who have had an organ transplant are prone to gout. Patients on numerous medicines should talk to their healthcare provider to see if there are interactions between medicine and if an alternate drug may help. The common vitamin niacin can also trigger gout.
Low carbohydrate diets, especially when very protein rich and with inadequate water intake can also cause gout. A family history of gout may also predispose a person towards getting it.